Understanding ASTM D149 Test for Dielectric Strength
When formulating materials to be used as a non-conductive barrier for high voltages, it is critical to ensure what they can withstand under various conditions. A material’s ability to resist electrical breakdown, known as its dielectric strength, is one such factor. The ASTM D149 standard is widely used to evaluate this. This test measures the dielectric breakdown voltage and dielectric strength of solid electrical insulating materials.
This test, when used alongside UV aging tests recommended by IEEE 1656, provides manufacturers a comprehensive look into just how well a material can maintain its ability to insulate over time. In this article, we will explore the significance of the ASTM D149 test, the effects of UV aging on dielectric performance, and the importance of conducting electrical insulation testing of ASTM D149 on both virgin and UV-aged materials.
What is ASTM D149 for Dielectric Strength?
The ASTM D149 standard evaluates the dielectric breakdown voltage of solid insulating materials. In other words, ASTM D149 measures how high of voltage a material can withstand before it fails. This test is useful in determining the safety of a material and whether or not it should be used in electrical applications. This test is typically conducted at commercial power frequencies for high voltage insulation testing.
The dielectric strength of a material is measured mainly in two metrics:
- Puncture Voltage (kV): The voltage at which the material breaks down or punctures.
- Volts per Mil (V/mil): The breakdown voltage per unit thickness of the material.
While it is recommended that material be tested at the same thickness as it is on a complete product, you may encounter test results based on material of varying thicknesses. Volts per Mil (V/mil) is an effective metric for evaluating the dielectric strength of insulating materials, indicating how much voltage a material can withstand per unit of thickness. This measurement providing a standardized metric to compare products across manufacturers as it provides a consistent basis for assessment regardless of material thickness. By standardizing how insulation performance is measured, this metric enables clearer, more informed choices in material selection, enhancing both product design and safety protocols.
How to Perform Dielectric Breakdown Test ASTM D149
The ASTM D149 dielectric breakdown test involves placing the material under controlled conditions where increasing voltage is applied until the material punctures. Ideally, this test should be performed on both virgin (unexposed) materials as well as materials that have been subjected to environmental factors, namely UV aging. This helps to simulate real-world conditions and is important to do as the amount of UV exposure a material has endured will affect its durability over time.
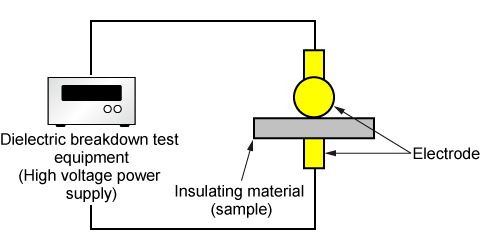
Source: MATSUSADA PRECISION
Testing Virgin and UV-Aged Material
The ASTM D149 high voltage electrical test allows for the evaluation of both new and aged materials. When this test is used in conjunction with other standards like IEEE 1656 where materials are subjected to UV exposure, it accurately simulates the durability of materials in real-world conditions. Years of exposure to environmental conditions such as sunlight can degrade dielectric properties. This test is commonly performed after 1,000 hours of UV exposure following ASTM D4329 and G154 guidelines.
Here is an example of how dielectric strength changes after UV aging:
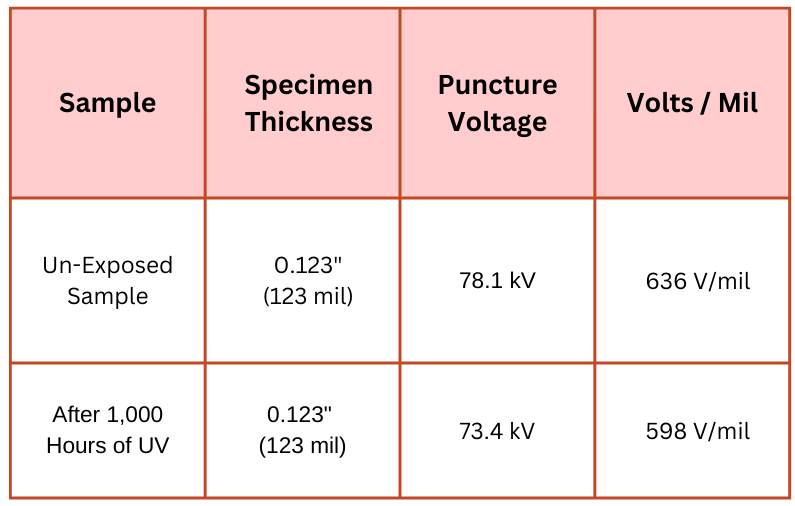
The slight decrease in puncture voltage and volts per mil after 1,000 hours of UV exposure shows that while there is some degradation, the material retains most of its dielectric strength. This provides confidence in the material’s long-term performance in outdoor environments.
Electrical Insulation Testing ASTM D149
High voltage insulation testing is important for many industries, including power utilities. Insulating materials are subject to mechanical stresses, environmental exposure, and high voltage, which means they need to maintain their dielectric strength over time. Along with the dielectric breakdown test, other electrical insulation testing methods such as tensile and impact strength tests are also conducted to assess mechanical properties.
Key mechanical tests that complement dielectric strength testing include:
- ASTM D256 & ASTM D4812: Impact Strength (notched and un-notched)
- ASTM D638: Tensile Strength, Elongation, and Modulus
- ASTM D790: Flexural Strength and Modulus
These tests provide a comprehensive understanding of how well the material will perform under various mechanical and electrical conditions, ensuring long-term reliability.
Understanding ASTM D149 Test Methods for Insulation
ASTM D149 testing involves subjecting materials to a slow, controlled rise in voltage until the dielectric breakdown occurs. The results determine whether the material can be used in demanding environments and applications like electrical utilities. This test is useful to do on insulation materials that must remain intact under extreme conditions.
Are Your Materials Up to Par?
The ASTM D149 standard is a valuable tool for evaluating the long-term performance of electrical insulation materials. ASTM D149 high voltage electrical testing, especially when used in conjunction with UV aging tests provides essential insights into a material’s durability in real-world environments. When evaluating products for installation on your network, take a look at these kinds of test results to determine the potential longevity of your investment.
At Rauckman Utility Products, we pride ourselves on the safety of our electrical materials and are proud to offer electrical insulation materials that meet the highest standards. To learn more or to request a quote, click here and one of our representatives will get in contact with you.